Working with ParConfigs and ParamSets
Jakob Richter
Source:vignettes/working_with_parconfigs_and_paramsets.Rmd
working_with_parconfigs_and_paramsets.RmdThis Vignette is covers the ParConfig objects, what they contain and how they are created.
Components of a ParConfig
First we will create a ParConfig so we can have a look at what we need.
ps = makeParamSet(
makeIntegerParam("k", lower = 1, upper = 20)
)
pc = makeParConfig(
learner = "classif.knn",
par.set = ps
)
str(pc, 1)## List of 6
## $ par.set :List of 2
## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "ParamSet"
## $ par.vals : NULL
## $ associated.learner.class: chr "classif.knn"
## $ associated.learner.type : chr "classif"
## $ associated.learner.name : chr "knn"
## $ note : chr ""
## - attr(*, "class")= chr "ParConfig"Now we already saw a minimal way to create a ParConfig out of a ParamSet and the according learner. Instead of the string "classif.knn" you can also directly pass the mlr learner object. We see that par.vals and note is not used.
-
par.valsis to store fixed parameter settings that we want to use to override the defaults of thelearner. -
noteis just for leaving a comment that will eventually be visible online once you decide to upload yourParConfig.
Access the components of a ParConfig
## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## k integer - - 1 to 20 - TRUE -## list()## [1] "classif.knn"## [1] "knn"## [1] "classif"getParConfigNote(pc)## [1] ""
Modify the components of a ParConfig
(pc.reg = setParConfigLearner(pc, "regr.kknn"))## Parameter Configuration
## Parameter Values:
## Associated Learner: regr.kknn
## Parameter Set:
## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## k integer - - 1 to 20 - TRUE -setParConfigLearnerType(pc.reg, "classif")## Parameter Configuration
## Parameter Values:
## Associated Learner: classif.kknn
## Parameter Set:
## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## k integer - - 1 to 20 - TRUE -setParConfigNote(pc.reg, "A note...")## Parameter Configuration
## Parameter Values:
## Associated Learner: regr.kknn
## Note: A note...
## Parameter Set:
## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## k integer - - 1 to 20 - TRUE -setParConfigParVals(pc.reg, list(scale = FALSE))## Parameter Configuration
## Parameter Values: scale=FALSE
## Associated Learner: regr.kknn
## Parameter Set:
## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## k integer - - 1 to 20 - TRUE -setParConfigParSet(pc.reg, makeParamSet(makeIntegerParam("k", 3, 11)))## Parameter Configuration
## Parameter Values:
## Associated Learner: regr.kknn
## Parameter Set:
## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## k integer - - 3 to 11 - TRUE -
Create a ParConfig
We already saw how to minimally create a ParConfig in the first example. Let’s look at more examples:
lrn = makeLearner("regr.kknn")
makeParConfig(
par.set = ps,
learner = lrn,
par.vals = list(kernel = "gaussian"),
note = "This is just an example with the kernel set to 'Gaussian'."
)## Parameter Configuration
## Parameter Values: kernel=gaussian
## Associated Learner: regr.kknn
## Note: This is just an example with the kernel set to 'Gaussian'.
## Parameter Set:
## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## k integer - - 1 to 20 - TRUE -
Create a ParConfig without a specific learner
mlr differentiates learners pretty strictly from their type (e.g. classification, regression, cluster etc.) although sometimes they share the same R function in the underlying package. If we want to allow the ParConfig to serve for classif.knn as well as regr.knn we have to construct it less strict like the following:
pc.less = makeParConfig(
learner.name = "knn",
par.set = ps
)
str(pc.less, 1)## List of 6
## $ par.set :List of 2
## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "ParamSet"
## $ par.vals : NULL
## $ associated.learner.class: NULL
## $ associated.learner.type : NULL
## $ associated.learner.name : chr "knn"
## $ note : chr ""
## - attr(*, "class")= chr "ParConfig"Or if you are unsure about the learner name but have the mlr learner object:
lrn = makeLearner("classif.knn")
pc.less = makeParConfig(
learner.name = getLearnerName(lrn),
par.set = ps
)
str(pc.less, 1)## List of 6
## $ par.set :List of 2
## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "ParamSet"
## $ par.vals : NULL
## $ associated.learner.class: NULL
## $ associated.learner.type : NULL
## $ associated.learner.name : chr "knn"
## $ note : chr ""
## - attr(*, "class")= chr "ParConfig"Note: The function generateParConfig will return a ParConfig for a given learner with a default tuning ParamSet.
The Basics of a ParamSet
Most of the power of a ParConfig lies it in the ParamSet which is part of the ParamHelpers package. The most important features will be explained in the following.
Creating a ParamSet
If we want to create a ParamSet for a specific mlr learner it is always helpful to check which parameters are available.
## Type len Def
## scaled logical - TRUE
## type discrete - C-svc
## kernel discrete - rbfdot
## C numeric - 1
## nu numeric - 0.2
## epsilon numeric - 0.1
## sigma numeric - -
## degree integer - 3
## scale numeric - 1
## offset numeric - 1
## order integer - 1
## tol numeric - 0.001
## shrinking logical - TRUE
## class.weights numericvector <NA> -
## fit logical - TRUE
## cache integer - 40
## Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## scaled - - TRUE -
## type C-svc,nu-svc,C-bsvc,spoc-svc,kbb-svc - TRUE -
## kernel vanilladot,polydot,rbfdot,tanhdot,lap... - TRUE -
## C 0 to Inf Y TRUE -
## nu 0 to Inf Y TRUE -
## epsilon -Inf to Inf Y TRUE -
## sigma 0 to Inf Y TRUE -
## degree 1 to Inf Y TRUE -
## scale 0 to Inf Y TRUE -
## offset -Inf to Inf Y TRUE -
## order -Inf to Inf Y TRUE -
## tol 0 to Inf - TRUE -
## shrinking - - TRUE -
## class.weights 0 to Inf - TRUE -
## fit - - FALSE -
## cache 1 to Inf - TRUE -Now we are facing two problems. First, these parameters don’t have finite box constraints and most tuning methods require finite box constraints. Second, there are quite many and tuning works best when only presented the most important tuning parameters. We will build our own ParamSet accordingly. The function makeParamSet will take any parameter and create a ParamSet object, which in our example would then be used to tune the ksvm model. To name the most important ones
makeNumericParam(id, lower, upper)makeIntegerParam(id, lower, upper)makeLogicParam(id)makeDiscreteParam(id, values)
ps.svm = makeParamSet(
makeNumericParam("C", lower = 0, upper = 100),
makeDiscreteParam("kernel", values = c("polydot","rbfdot"))
)Attention! Here we see the first problem: The parameter C is more sensitive to changes for values around zero. We will use the trafo argument of makeNumericParam()so that our search space for C accounts for the sensitivity near zero.
Creating a ParamSet with a transformation
ps.svm.trafo = makeParamSet(
makeNumericParam("C", lower = -5, upper = 7, trafo = function(x) 2^x),
makeDiscreteParam("kernel", values = c("polydot","rbfdot"))
)Let’s compare randomly drawn values:
s1 = sampleValues(ps.svm, n = 100)
s2 = sampleValues(ps.svm.trafo, n = 100, trafo = TRUE)
op = par(mfrow = c(1,2))
hist(BBmisc::extractSubList(s1, "C"))
hist(BBmisc::extractSubList(s2, "C"))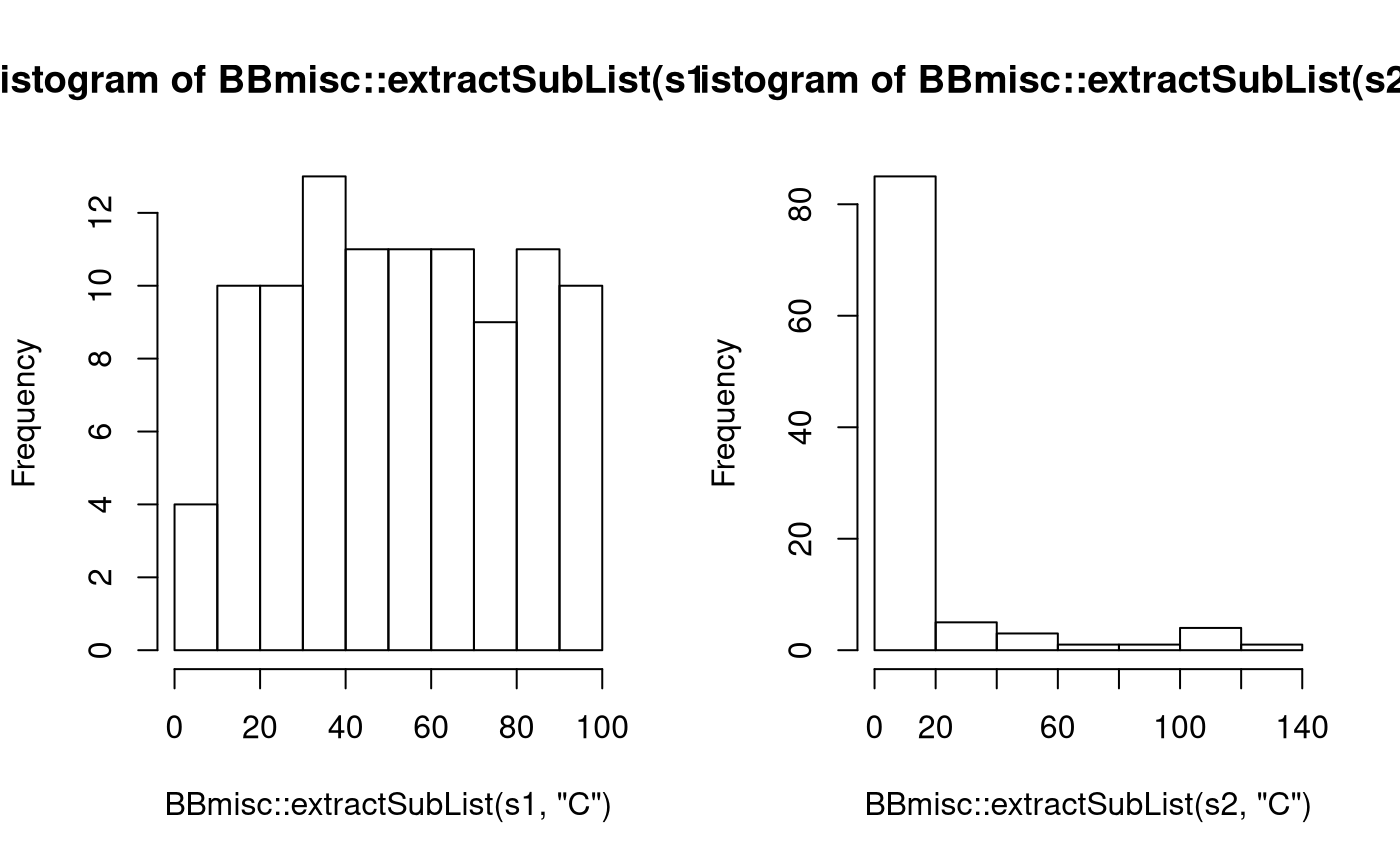
par(op)As transformations can be arbitrary functions they can be used for other useful purposes as only generating uneven numbers, which makes sense for knn classification to not have ties:
Creating a ParamSet with dependent / hierarchical parameters
For our SVM example we actually would like to tune the parameter sigma for the rbfdot kernel and the degree for the polydot kernel. So the sigma parameter should only be active when kernel is set to rbfdot and degree should only be active for kernel == "polydot". To model such dependencies or hierarchical structures in the parameter space all make*Param functions have the requires argument which can be used like follows:
ps.svm.req = makeParamSet(
makeNumericParam("C", lower = -5, upper = 7, trafo = function(x) 2^x),
makeDiscreteParam("kernel", values = c("polydot","rbfdot")),
makeNumericParam("sigma", lower = -5, upper = 5, trafo = function(x) 2^x, requires = quote(kernel == "rbfdot")),
makeIntegerParam("degree", lower = 1, upper = 5, requires = quote(kernel == "polydot"))
)Let’s generate a LHS design to see the effects of the requirements:
## C kernel sigma degree
## 1 -1.2177714 polydot NA 2
## 2 3.3209502 rbfdot -3.411498 NA
## 3 5.6590948 polydot NA 1
## 4 1.2163571 rbfdot 3.499076 NA
## 5 -0.4340143 polydot NA 4
## 6 -3.2670645 rbfdot 2.933999 NA
Creating a ParamSet with data dependent parameter spaces
For some learners the tuning space varies from the data presented. A prominent example is the mtry parameter of the randomForest which determines how many randomly drawn variables are to be considered in every split. The default is sqrt(p) with p being the number of variables in the data. Naturally we might want to set the boundaries for that value around that default. This is possible using expressions like in the following example:
ps.rf = makeParamSet(
makeIntegerParam("mtry", lower = expression(floor(sqrt(p*0.25))), upper = expression(ceiling(sqrt(p*0.75))))
)Which variables can I use in the expressions?
getTaskDictionary(task = iris.task)## $task
## Supervised task: iris-example
## Type: classif
## Target: Species
## Observations: 150
## Features:
## numerics factors ordered functionals
## 4 0 0 0
## Missings: FALSE
## Has weights: FALSE
## Has blocking: FALSE
## Has coordinates: FALSE
## Classes: 3
## setosa versicolor virginica
## 50 50 50
## Positive class: NA
##
## $p
## [1] 4
##
## $n.task
## [1] 150
##
## $type
## [1] "classif"
##
## $n
## [1] 150
##
## $k
## [1] 3
##
## $t
## setosa versicolor virginica
## 50 50 50-
pnumber of features / variables in x -
n.tasknumber of observations in the task -
typetype of the task likeclassif,regr,clusterandsurv. -
nnumber of observations in the subset -
knumber of classes in target -
taskthe complete task object
Attention: This feature is not implemented in mlr yet. As a consequence, the expressions have to be pre-evaluated before they can be used for tuning. This also means that n will always be the tasks data set size instead of the number of observations after a cross-validation split. Feature selection will not affect p.
To convert the ParamSet with expressions to a normal ParamSet we call the following:
evaluateParamExpressions(ps.rf, dict = getTaskDictionary(iris.task))## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## mtry integer - - 1 to 2 - TRUE -evaluateParamExpressions(ps.rf, dict = list(p = 100, n = 1000))## Type len Def Constr Req Tunable Trafo
## mtry integer - - 5 to 9 - TRUE -